Geopolitical instability
The Russian war of aggression against Ukraine, the ongoing situation in the Middle East, and an elevated threat level from illegal intelligence activities are driving forces behind the altered global security situation. Hence, awareness of energy security and self-sufficiency in Europe and Norway has increased.
The power grid is critical infrastructure, and even short interruptions may cause significant consequences for essential societal functions. Consequently, digital and physical security, a robust power grid, and the ability to restore systems in case of outages is crucial.
Energy transition
In Europe, the energy transition continues at a rapid pace, particularly the development of renewable power production. Statnett’s Short-Term Market Analysis 2024-2029 (in Norwegian) states that approximately 85 GW of solar and wind power were established in Europe in 2023, and 90 GW will be installed in 2024.
At the same time, the growth in European power consumption is slower than previously anticipated due to the time required for electrification and increased global competition for green industries from countries such as China and the USA.
This trend is also evident in Norway with a stable national power consumption in recent years. At the same time, electrification and new industries remain driving forces behind the ongoing backlog in grid connection. In the final quarter of 2024, the connection backlog consists of customers equivalent to more than 20.000 MW.
As a result, the scenarios in Statnett’s Long-Term Market Analysis 2024 predicts significant consumption growth, though somewhat delayed compared to the previous analysis.
The need for upgrading transmission channels remains, and Statnett will perform the upgrades to meet future demand and balance out the price variations in the power system. In addition, the majority of upgrades are necessary due to the technical condition of the facilities: about 50 percent of Statnett’s gridlines will reach end-of-life by 2040.
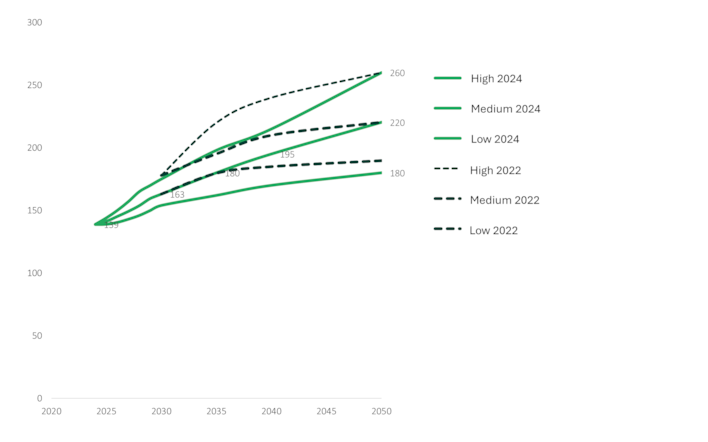
Statnett has invested a total of 92 billion NOK in grid and digital projects during the period 2014-2024. Over the next decade, Statnett plans to double these investments. Any investments in offshore grid will be additional.
Challenging supplier markets
Shifts in geopolitical conditions affects the global supply chains and causes potential vulnerability.
Europe is reinforcing and expanding its transmission grid, and this leads to high demand, long lead times for components and raw materials, and increased prices.
Responsible transition requirements
New expectations towards preserving nature, people and local communities are rapidly emerging in society. Valuation of nature and involvement of stakeholders at an early stage reduces risk of conflict and enhances efficiency in project execution.
Furthermore, conflict of interest prolongs the duration of permitting processes. In a challenging market defined by high demand and global supply chains, the risk of human rights violations increases, along with the need for strategic sourcing.
Climate change is a major threat and ensuring energy security requires making our facilities resilient to climate change and more frequent extreme weather events.
Automated power system
The Norwegian Power system is closely integrated with the Nordic and Northern-European systems through physical and digital connections and the common electricity market. Shifts in the European system will affect the Norwegian, and vice versa.
An increased share of intermittent and renewable power leads to a more volatile power system that is challenging to regulate and changes its technical characteristics.
This creates challenging operating conditions of the power system and calls for automation applications and systems along with proper electricity market mechanisms.